Triggers
A trigger is an event that causes a sensor to take a single 3D snapshot. You configure triggers on the Acquire > Scan page.

When a trigger is processed, the LED light pattern is strobed and the cameras expose to produce images. The resulting images are processed inside the sensor to yield a 3D point cloud.
At the top-right of the Scan page, the maximum frame rate is displayed, based on the exposure values, active area, the number of projection patterns required, and so on.
The sensor can be triggered by one of the sources described below.

|
If the sensor is connected to a Master 400 or higher, encoder and digital (external) input signals over the IO cordset are ignored. The sensor instead receives these signals from the Master; for encoder and digital input pinouts on Masters, see the section corresponding to your Master in Master Network Controllers. If the sensor is connected to a Master 100 (or no Master is used), the sensor receives signals over the IO cordset. For information on connecting encoder and digital input signals to a sensor in these cases, see Encoder Input and Digital Input, respectively. |
When using encoder triggering (available with line profilers), the current encoder resolution is displayed under the Source drop-down as a reference when setting trigger spacing.
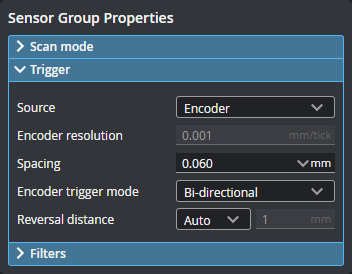
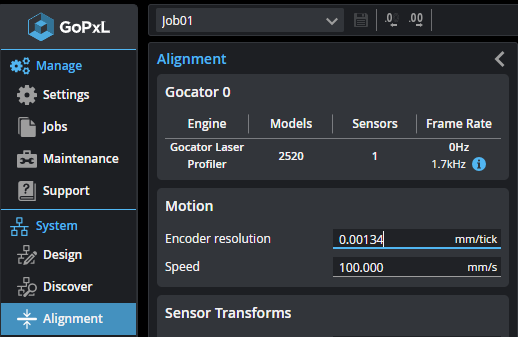
To set the encoder resolution, go to the System > Alignment page and set the value in Encoder Resolution.
| Trigger Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Time |
Sensors have an internal clock that can be used to generate fixed-frequency triggers. The external input can be used to enable or disable the time triggers. |
| External Input |
A digital input can provide triggers in response to external events (for example, a photocell). The external input triggers on the rising edge of the signal. When triggers are received at a frequency higher than the maximum frame rate, some triggers may not be accepted. Use the Trigger Drops indicator in the Health panel on the Reports page to check for this condition; for more information, see Reporting. For information on the maximum input trigger rate, see Maximum Input Trigger Rate. |
| Software |
A network command can be used to send a software trigger. For more information, Protocols (PLCs and other hardware). |
For examples of typical real-world scenarios, see Trigger Examples.
Trigger Settings
After you choose the trigger source, configure the other parameters in the Trigger section on the Scan page.
| Parameter | Trigger Source | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Source |
n/a |
Selects the trigger source (Time, External Input, or Software). |
|
Trigger at maximum frame rate |
Time |
When this is enabled, the frame rate locks to the maximum frame rate. |
|
Frame Rate |
Time |
Controls the frame rate. Fractional values are supported. For example, 0.1 can be entered to run at 1 frame every 10 seconds. |
| Trigger Delay | External Input |
Specifies the amount of time or the distance the sensor waits before producing a frame after the external input is activated. This is used to compensate for the positional difference between the source of the external input trigger (for example, a photocell) and the sensor. |